Appearance
像素着色器块
碎片块必须用于控制材料的碎片着色阶段。片段块必须包含有效的ESSL 3.0代码(OpenGL ES 3.0中支持的GLSL版本)。你可以自由地在fragment块中创建多个函数,但是你必须声明material函数:
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
prepareMaterial(material);
// fragment shading code
}
}这个函数将在运行时由着色系统自动调用,并使您能够使用MaterialInputs结构读取和修改材料属性。结构的完整定义可以在材料片段输入部分找到。结构的各种成员的完整定义可以在本文档的材质模型部分找到。
material()函数的目标是计算特定于所选着色模型的材料属性。例如,这里有一个碎片块,它使用标准光照阴影模型创建了一个光滑的红色金属:
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
prepareMaterial(material);
material.baseColor.rgb = vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
material.metallic = 1.0;
material.roughness = 0.0;
}
}prepareMaterial函数
注意,必须在退出material()函数之前调用prepareMaterial(material)。这个prepareMaterial函数设置材质模型的内部状态。像素着色器中一些API函数或属性的使用——例如shading_normal——只能在调用prepareMaterial()之后访问。
同样重要的是要记住,normal属性(如Material片段输入部分所述)只有在调用prepareMaterial()之前修改时才有效。下面是一个片段着色器的例子,它正确地修改了normal属性,以实现带有凹凸贴图的光滑红色塑料:
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
// fetch the normal in tangent space
vec3 normal = texture(materialParams_normalMap, getUV0()).xyz;
material.normal = normal * 2.0 - 1.0;
// prepare the material
prepareMaterial(material);
// from now on, shading_normal, etc. can be accessed
material.baseColor.rgb = vec3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
material.metallic = 0.0;
material.roughness = 1.0;
}
}Material fragment inputs
struct MaterialInputs {
float4 baseColor; // default: float4(1.0)
float4 emissive; // default: float4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
float4 postLightingColor; // default: float4(0.0)
// no other field is available with the unlit shading model
float roughness; // default: 1.0
float metallic; // default: 0.0, not available with cloth or specularGlossiness
float reflectance; // default: 0.5, not available with cloth or specularGlossiness
float ambientOcclusion; // default: 0.0
// not available when the shading model is subsurface or cloth
float3 sheenColor; // default: float3(0.0)
float sheenRoughness; // default: 0.0
float clearCoat; // default: 1.0
float clearCoatRoughness; // default: 0.0
float3 clearCoatNormal; // default: float3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
float anisotropy; // default: 0.0
float3 anisotropyDirection; // default: float3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
// only available when the shading model is subsurface or refraction is enabled
float thickness; // default: 0.5
// only available when the shading model is subsurface
float subsurfacePower; // default: 12.234
float3 subsurfaceColor; // default: float3(1.0)
// only available when the shading model is cloth
float3 sheenColor; // default: sqrt(baseColor)
float3 subsurfaceColor; // default: float3(0.0)
// only available when the shading model is specularGlossiness
float3 specularColor; // default: float3(0.0)
float glossiness; // default: 0.0
// not available when the shading model is unlit
// must be set before calling prepareMaterial()
float3 normal; // default: float3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
// only available when refraction is enabled
float transmission; // default: 1.0
float3 absorption; // default float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
float ior; // default: 1.5
float microThickness; // default: 0.0, not available with refractionType "solid"
}自定义的表面Shading
customSurfaceShading在材质块中被设置为true时,片段块必须声明并实现surfaceShading函数:
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
prepareMaterial(material);
// prepare material inputs
}
vec3 surfaceShading(
const MaterialInputs materialInputs,
const ShadingData shadingData,
const LightData lightData
) {
return vec3(1.0); // output of custom lighting
}
}此函数将被场景中可能影响当前片段的每个光(方向、点或点)调用。surfaceShading使用3组数据调用:
- MaterialInputs,如Material fragment inputs一节所述,并在上面解释的Material函数中准备
- ShadingData,一个包含从MaterialInputs派生值的结构(见下文)
- LightData,一个包含当前正在计算的特定光的值的结构(见下文)
surfaceShading函数必须返回线性sRGB的RGB颜色。Alpha混合和Alpha遮罩在此函数之外处理,因此必须忽略。
- Shading data structure
struct ShadingData {
// The material's diffuse color, as derived from baseColor and metallic.
// This color is pre-multiplied by alpha and in the linear sRGB color space.
vec3 diffuseColor;
// The material's specular color, as derived from baseColor and metallic.
// This color is pre-multiplied by alpha and in the linear sRGB color space.
vec3 f0;
// The perceptual roughness is the roughness value set in MaterialInputs,
// with extra processing:
// - Clamped to safe values
// - Filtered if specularAntiAliasing is enabled
// This value is between 0.0 and 1.0.
float perceptualRoughness;
// The roughness value expected by BRDFs. This value is the square of
// perceptualRoughness. This value is between 0.0 and 1.0.
float roughness;
};- Light data structure
struct LightData {
// The color (.rgb) and pre-exposed intensity (.w) of the light.
// The color is an RGB value in the linear sRGB color space.
// The pre-exposed intensity is the intensity of the light multiplied by
// the camera's exposure value.
vec4 colorIntensity;
// The normalized light vector, in world space (direction from the
// current fragment's position to the light).
vec3 l;
// The dot product of the shading normal (with normal mapping applied)
// and the light vector. This value is equal to the result of
// saturate(dot(getWorldSpaceNormal(), lightData.l)).
// This value is always between 0.0 and 1.0. When the value is <= 0.0,
// the current fragment is not visible from the light and lighting
// computations can be skipped.
float NdotL;
// The position of the light in world space.
vec3 worldPosition;
// Attenuation of the light based on the distance from the current
// fragment to the light in world space. This value between 0.0 and 1.0
// is computed differently for each type of light (it's always 1.0 for
// directional lights).
float attenuation;
// Visibility factor computed from shadow maps or other occlusion data
// specific to the light being evaluated. This value is between 0.0 and
// 1.0.
float visibility;
};- 一个例子: 下面的材料展示了如何使用自定义表面着色来实现一个简化的卡通着色器
material {
name : Toon,
shadingModel : lit,
parameters : [
{
type : float3,
name : baseColor
}
],
customSurfaceShading : true
}
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
prepareMaterial(material);
material.baseColor.rgb = materialParams.baseColor;
}
vec3 surfaceShading(
const MaterialInputs materialInputs,
const ShadingData shadingData,
const LightData lightData
) {
// Number of visible shade transitions
const float shades = 5.0;
// Ambient intensity
const float ambient = 0.1;
float toon = max(ceil(lightData.NdotL * shades) / shades, ambient);
// Shadowing and attenuation
toon *= lightData.visibility * lightData.attenuation;
// Color and intensity
vec3 light = lightData.colorIntensity.rgb * lightData.colorIntensity.w;
return shadingData.diffuseColor * light * toon;
}
}渲染结果如下: 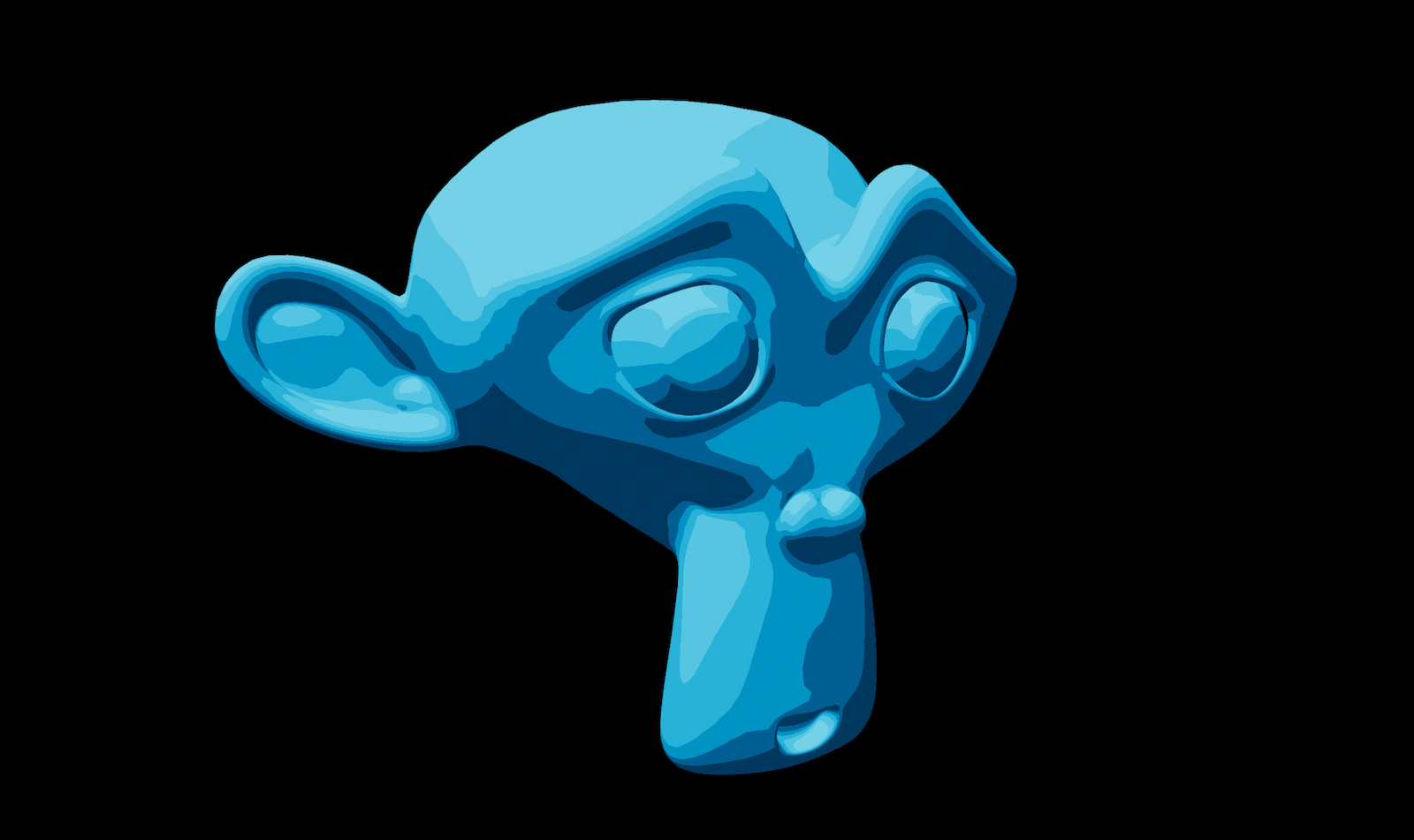
!!! Note: 即使已知片段完全处于当前光线(lightData)的阴影中,也会调用surfaceShading函数。NdotL <= 0.0或lightData。可见性<= 0.0)。这为surfaceShading功能提供了更多的灵活性,因为它提供了一种简单的方法来处理恒定的环境照明。
!!! Note: 自定义表面着色仅适用于光照着色模型。尝试使用任何其他模型都将导致错误。